Few topics spark as much curiosity and concern as deepfakes. These hyper realistic digital fabrications have moved far beyond novelty, influencing public opinion, enabling fraud, and eroding trust in digital media. As creators, security leaders, and technologists, we face a growing responsibility to understand how deepfakes work and how to detect them reliably at scale.
In this guide, we break down how deepfakes are created, why detection matters, the technologies used to identify them, and where the future of deepfake detection is heading.
Key Takeaways
- Deepfake detection is critical for combating misinformation, financial fraud, and identity abuse
- Machine learning, biometric analysis, and multi modal detection are core to modern defense strategies
- Combining automated detection with human review improves accuracy and reduces false positives
- Detection systems must adapt rapidly as deepfake generation techniques evolve
- Real time, privacy preserving detection is emerging as the next frontier
Understanding Deepfakes and Their Impact
Deepfakes are synthetic media generated using artificial intelligence to convincingly replicate real people in audio, video, or images. These fabrications often appear authentic to the human eye and ear, making them particularly dangerous.
The impact extends across industries:
- Fake executive voices used in financial fraud
- Manipulated videos influencing elections or public discourse
- Synthetic identities enabling large scale identity theft
- Harassment and non consensual media targeting individuals
As deepfakes become easier to create, organizations that fail to detect them face reputational damage, regulatory exposure, and financial loss.

How Deepfakes Are Created
Most deepfakes are produced using Generative Adversarial Networks. These systems rely on two neural networks competing against each other.
The process typically includes:
- Collecting large datasets of real audio or video
- Training models to replicate facial movements, speech patterns, and expressions
- Refining outputs until the fake becomes difficult to distinguish from reality
Open source tools and consumer apps have dramatically lowered the barrier to entry, making deepfake creation accessible to non experts.
Why Detecting Deepfakes Matters
Deepfake detection is not optional anymore. It is foundational to digital trust.
Key risks include:
- Misinformation and reputation damage
- Executive impersonation and payment fraud
- Synthetic identity creation at scale
- Erosion of trust in legitimate digital evidence
In regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and media, failure to detect deepfakes can have legal and operational consequences.
Core Technologies Used in Deepfake Detection
Machine Learning Based Detection
Machine learning models are trained on vast datasets of real and manipulated media to identify subtle anomalies.
Common techniques include:
- Convolutional Neural Networks for image and video analysis
- Temporal analysis to detect inconsistencies across video frames
- Audio signal analysis to identify synthetic speech artifacts
These systems operate at scale and detect patterns invisible to humans.
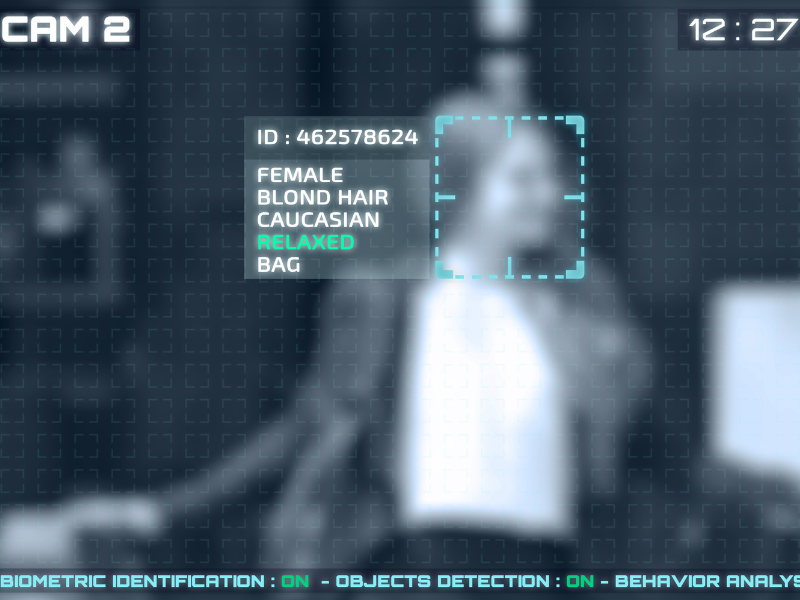
Forensic and Biometric Analysis
Forensic techniques add scientific rigor and context.
These include:
- Pixel and compression artifact analysis
- Metadata validation and provenance checks
- Biometric signals such as blink rates, speech cadence, or micro expressions
Modern detection platforms increasingly combine biometric signals with AI analysis to improve confidence.
This is where solutions like PrivateID’s MediaSafe facial biometric tracking and deepfake detection become relevant. MediaSafe analyzes live video streams using privacy preserving biometric signals to identify manipulated or synthetic faces in real time, without storing or transmitting biometric images.
Human and Automated Detection Working Together
Neither humans nor machines are sufficient alone.
- Automated systems provide speed, scale, and consistency
- Human reviewers contribute contextual judgment and intent analysis
The most effective detection pipelines use AI to flag high risk content, followed by expert human review for validation.
Current Challenges in Deepfake Detection
Despite progress, detection faces ongoing challenges:
- Rapid evolution of generation techniques
- Generalization issues when models encounter new deepfake types
- Adversarial attacks designed to bypass detectors
- High computational requirements for real time analysis
Detection is an arms race, requiring continuous learning and adaptation.
Emerging Trends and Research Directions
Innovation in deepfake detection is accelerating.
Key developments include:
- Multi modal fusion combining audio, video, and metadata
- Explainable AI to support legal and regulatory review
- Blockchain based provenance tracking
- Edge based detection for real time video streams
Privacy preserving approaches are also gaining importance. On device processing and anonymized biometric analysis reduce risk while maintaining accuracy, an approach already reflected in PrivateID’s architecture.
Legal, Ethical, and Social Considerations
Detection is not purely technical.
Key considerations include:
- Balancing security with privacy rights
- Avoiding overreach or surveillance abuse
- Preserving free expression while limiting harm
- Establishing accountability for misuse
Clear standards and transparent detection practices are essential to maintain public trust.
The Future of Deepfake Detection
Looking ahead, effective detection will be:
- Real time rather than reactive
- Integrated directly into media platforms and identity workflows
- Supported by global standards and collaboration
- Privacy preserving by design
As deepfakes grow more sophisticated, detection must evolve just as quickly, without compromising civil liberties or data protection.
Conclusion
Deepfakes represent one of the most complex challenges of the modern digital era. Detecting them requires a blend of advanced technology, human judgment, ethical frameworks, and cross industry cooperation.
By investing in scalable, privacy conscious detection systems and educating users, we can protect trust in digital media and ensure innovation continues responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions About Deepfake Detection
What is deepfake detection and why is it important?
Deepfake detection involves identifying digitally manipulated audio, video, or images created using AI. Detecting deepfakes is crucial because they can spread misinformation, enable fraud, erode public trust, and harm reputations and privacy across society.
What are the main challenges in deepfake detection?
Challenges include the rapid evolution of deepfake technology, a lack of diverse training data, adversarial attacks specifically engineered to fool detection systems, and the high computational resources required for accurate identification.
Can humans reliably detect deepfakes without automated tools?
While humans can sometimes spot contextual oddities or behavioral cues, highly sophisticated deepfakes are often indistinguishable without automated tools. The best systems combine machine analysis and expert human review for maximum accuracy.
What are emerging trends in deepfake detection technology?
Emerging trends include real-time detection using edge AI, blockchain-based verification for digital provenance, explainable AI for transparency, multi-modal fusion combining several data types, and crowdsourced reporting to enhance detection efforts.
How can individuals protect themselves from deepfake scams?
Individuals should verify content from trusted sources, be cautious with unsolicited communications, use reputable fact-checking tools, and stay informed about deepfake detection developments to avoid falling victim to scams and misinformation.